dlp 3d printer pictures drawing
In that location are many 3D printing processes on the market. Getting familiar with the nuances of each helps to clarify what you can expect from final prints to ultimately decide which technology is suitable for your detail application.
Stereolithography (SLA) and digital calorie-free processing (DLP) 3D printing are the two most common processes for resin 3D press. Resin 3D printers are popular for producing high-accuracy, isotropic, and watertight prototypes and parts in a range of advanced materials with fine features and smooth surface end.
While these technologies were once circuitous and toll-prohibitive, today's pocket-size-format desktop SLA and DLP 3D printers produce industrial-quality parts at an affordable price point and with unmatched versatility thanks to a broad range of materials.
Both processes work by selectively exposing liquid resin to a low-cal source—SLA a light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation, DLP a projector—to form very sparse solid layers of plastic that stack up to create a solid object. While very like in principle, the ii technologies can produce significantly varying outputs.
In this in-depth guide, we walk through the details of the two resin 3D printing processes and explore how they compare in terms of resolution, accuracy, build book, speed, workflow, and more than.

Desktop SLA 3D printers contain a resin tank with a transparent base and non-stick surface, which serves equally a substrate for the liquid resin to cure confronting, allowing for the gentle detachment of newly-formed layers.
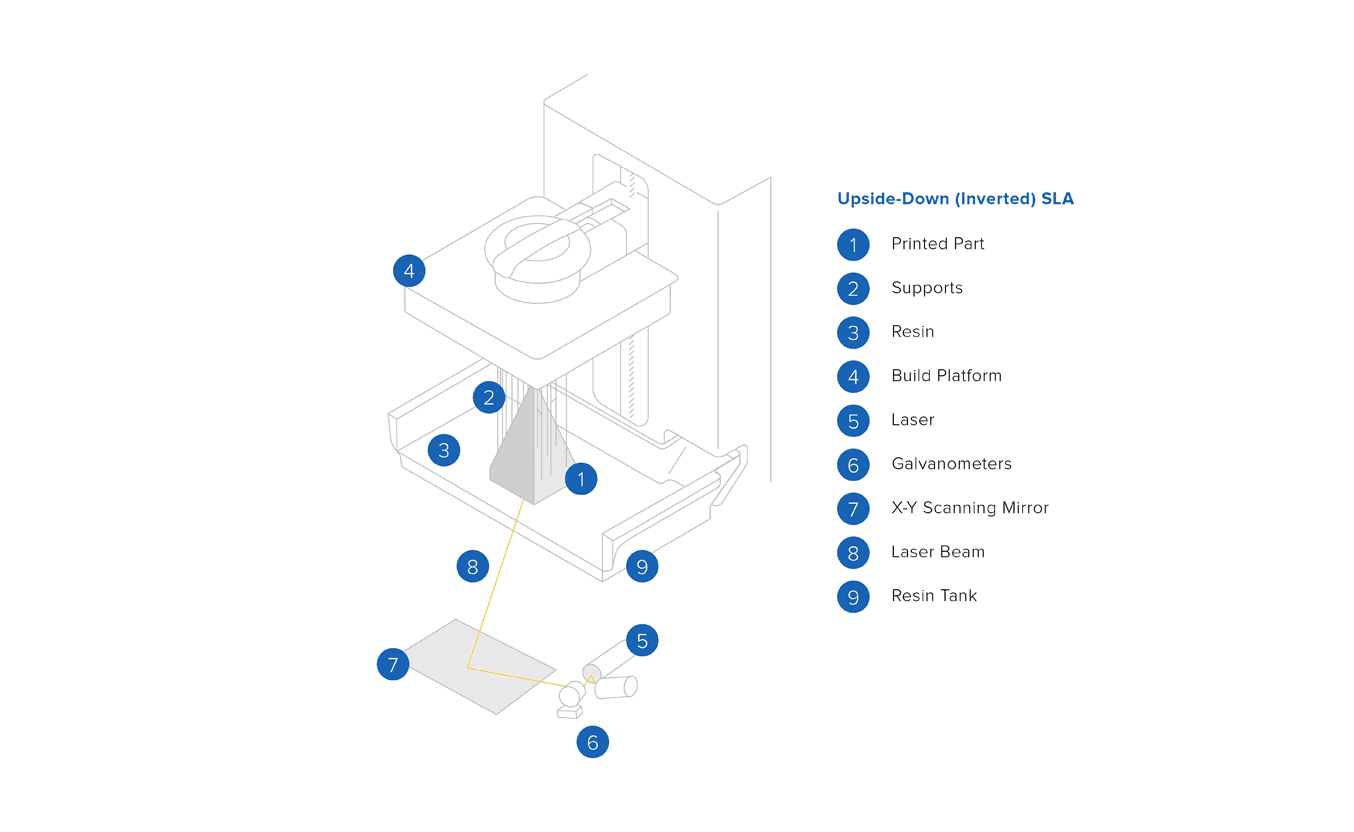
The printing process starts as the build platform descends into a resin tank, leaving space equal to the layer acme in betwixt the build platform, or the last completed layer, and the lesser of the tank. A laser points at two mirror galvanometers, which direct the low-cal to the right coordinates on a series of mirrors, focusing the low-cal upward through the lesser of the tank and curing a layer of resin.
The cured layer and then gets separated from the lesser of the tank and the build platform moves up to permit fresh resin menses beneath. The process repeats until the print is complete.
Low Force Stereolithography (LFS) technology, used past the Form 3 and Form 3L, is the adjacent phase in SLA 3D printing.
In LFS 3D printers, the optics are enclosed in a Light Processing Unit (LPU). Within the LPU, a galvanometer positions the high-density laser beam in the Y direction, passes information technology through a spatial filter, and directs information technology to a fold mirror and parabolic mirror to consistently deliver the axle perpendicular to the build plane and ensure accurate, repeatable prints.
As the LPU moves in the 10 direction, the printed part is gently peeled away from the flexible bottom of the tank, which drastically reduces the forces exerted on parts during the print process.
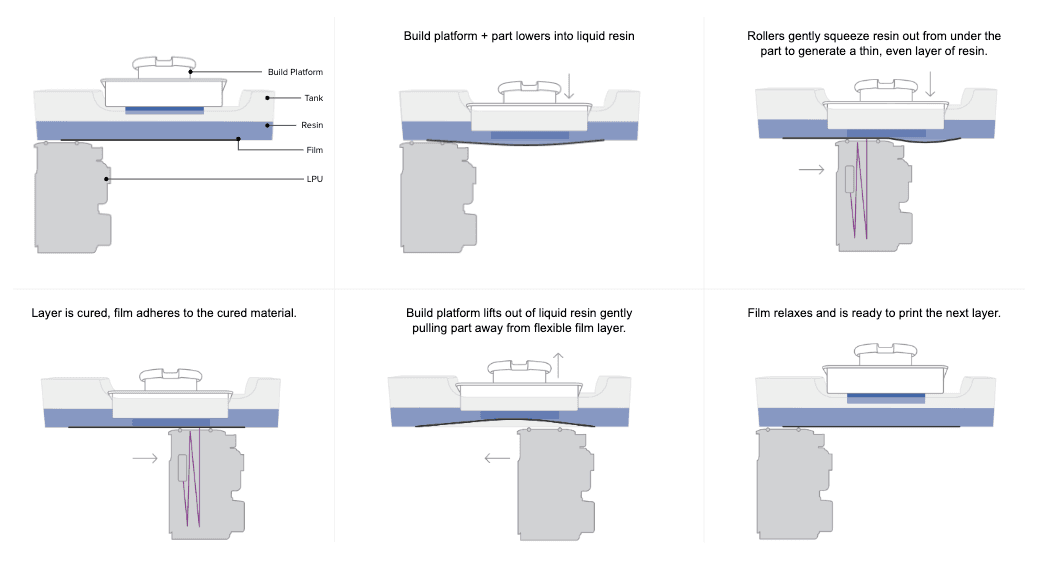
LFS 3D printing drastically reduces the forces exerted on parts during the impress process, using a flexible tank and linear illumination to deliver incredible surface quality and print accuracy.
This advanced class of stereolithography delivers vastly improved surface quality and print accuracy. Lower print forces also allow for calorie-free-touch support structures that tear away with ease, and the process opens up a wide range of possibilities for future development of avant-garde, production-ready materials.
Resolution shows up more oftentimes than any other value in 3D printer spec sheets, but it's besides a common ground for confusion. The bones units of the SLA and DLP processes are different shapes, making it difficult to compare the different machines by numerical specifications lone.
In 3D press, there are three dimensions to consider: the two planar 2D dimensions (X and Y) and the tertiary vertical Z dimension that makes 3D printing.
Z resolution is defined by the layer thicknesses a 3D printer tin produce. Resin 3D printers like SLA and DLP offer some of the finest Z resolutions—thinnest layers—of all 3D printing processes and users can normally cull from a range of layer superlative options betwixt 25-300 microns, allowing designers to strike a balance between detail and speed.
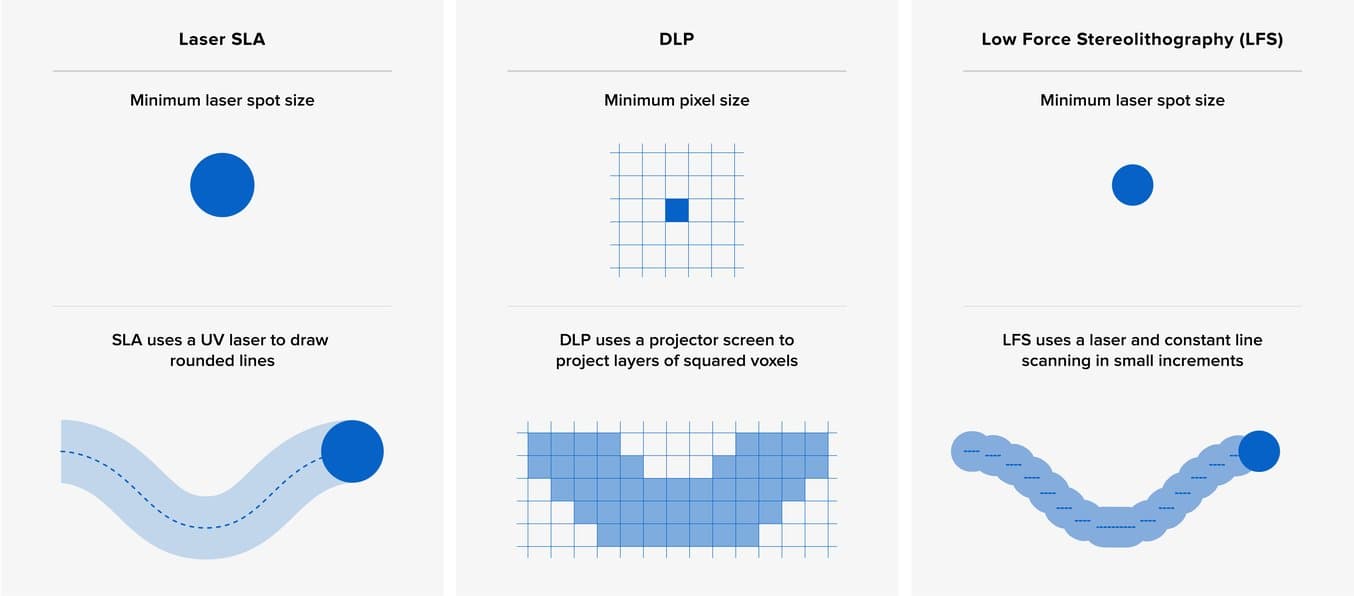
In DLP 3D printing, XY resolution is divers by the pixel size, the smallest characteristic the projector tin reproduce inside a single layer. This depends on the resolution of the projector, the most common existence full Hd (1080p), and its distance from the optical window. Equally a result, almost desktop DLP 3D printers have a fixed XY resolution, generally between 35 to 100 microns.
For SLA 3D printers, XY resolution is a combination of the laser's spot size and the increments past which the laser beam tin be controlled. For example, the Form 3 LFS 3D printer features a light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation with an 85 micron spot size, but because of the constant line scanning procedure, the light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation tin can move in smaller increments and the printer can consistently deliver parts with 25 micron XY resolution.
However, resolution in itself is frequently simply a vanity metric. It offers some indication, just it doesn't necessarily correlate directly with accuracy, precision, and impress quality.
Learn more than nigh resolution in 3D printing in our in-depth guide.
Because 3D printing is an condiment process, each layer introduces an opportunity for inaccuracy, and the process by which layers are formed affects the level of precision, defined as the repeatability of the accuracy of each layer. Accuracy and precision depend on many unlike factors: 3D printing process, materials, software settings, post-processing, and more.
In full general, both SLA and DLP resin 3D printers are amid the most accurate and precise 3D press processes. Differences in accuracy and precision are often ameliorate explained by the differences betwixt machines past diverse manufacturers than differences betwixt the technologies themselves.
For instance, entry-level SLA or DLP printers might use off-the-shelf projectors, lasers, or galvanometers, and their manufacturers will try to get the best functioning possible out of these parts. Professional SLA and DLP 3D printers, like the Formlabs Class iii, feature a custom optical organisation adapted to the specifications required by professional customer applications.
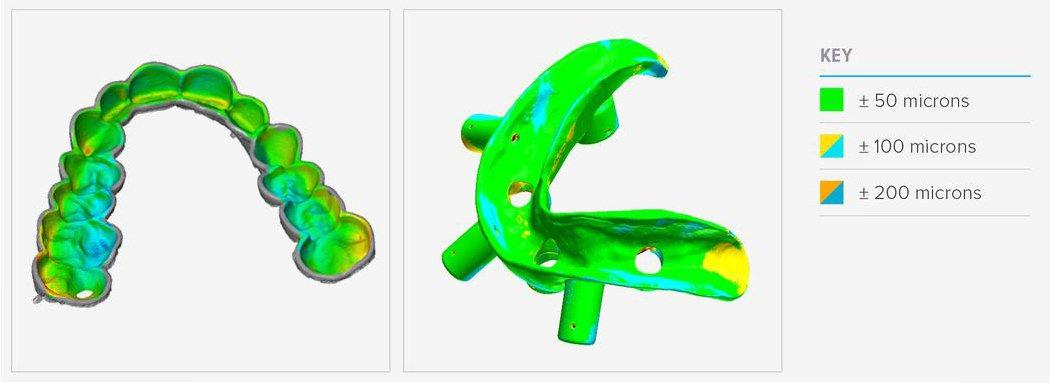
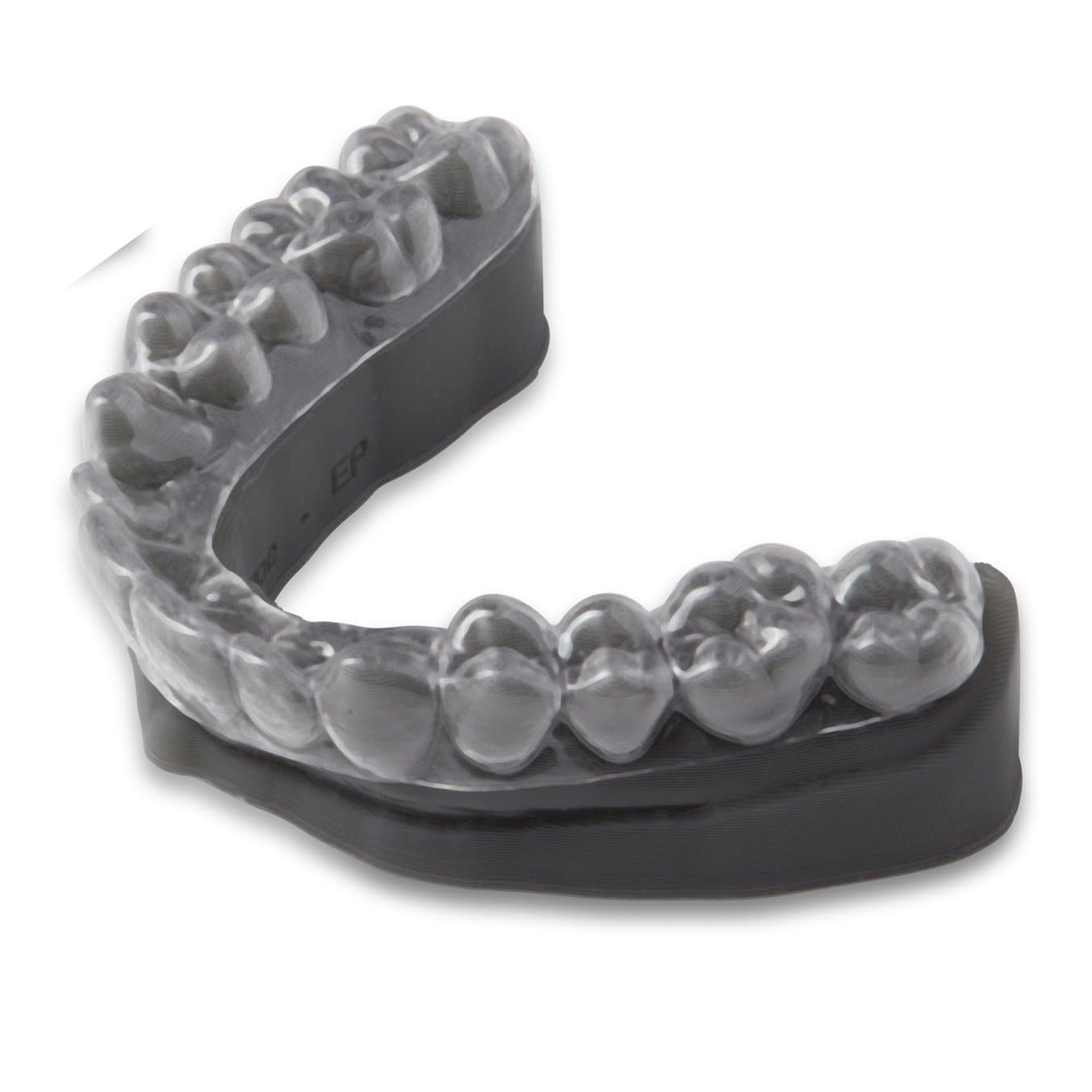
Accuracy and precision are crucial for parts similar dental splints (left) and surgical guides (right).
Calibration is likewise crucial. With DLP projectors, manufacturers need to bargain with the non-uniform lite distribution on the build plane and optical baloney of the lenses—significant that pixels in the center are not the same size or shape as pixels on the edges. SLA 3D printers use the same light source for every function of the print, which means it'south uniform by definition, but they still require extensive scale to account for distortions.
Even a 3D printer with the highest quality components and degree of scale tin produce widely varying results depending on the material. Different resins require optimized material settings to perform as intended, which might non exist available for off-the-shelf materials or resins that are not thoroughly tested with a specific 3D printer model.
The takeaway? Accuracy and precision are almost impossible to empathise from the technical specifications alone. Ultimately, the all-time way to evaluate a 3D printer is to audit real parts or ask the manufacturer to create a test print of ane of your ain designs.
With DLP 3D printers, there'southward a direct trade-off betwixt resolution and build volume. The resolution depends on the projector, which defines the number of pixels/voxels bachelor. If one moves the projector closer to the optical window, the pixels go smaller, which increases the resolution, but limits the available build area.
Some manufacturers stack multiple projectors next to each other or use a loftier-definition 4K projector to increase the build book, but this leads to essentially higher costs that often toll these machines out of the desktop market.
As a result, DLP 3D printers are generally optimized for specific use cases. Some have a smaller build volume and offering high resolution to produce small, detailed pieces similar jewelry, while others tin produce bigger parts just at a lower resolution.
The stereolithography process is inherently more scalable, since an SLA 3D printer's build volume is completely independent of the resolution of the print. A single print can be any size and whatsoever resolution at any location inside the build area. This makes it possible to 3D impress large parts at high resolution or a big batch of detailed minor parts to increase throughput with the same automobile.
The other main barrier to increasing build book in both SLA and DLP 3D printers is the skin force. When press larger parts, the forces exerted on the parts increase exponentially every bit a cured layer separates from the tank.
In LFS 3D printing, the flexible motion picture at the base of the resin tank gently peels away as the build platform pulls the role up, significantly reducing the stress on the part. This unique feature has made information technology possible to substantially increase the build volume for the first accessible large format SLA 3D printer, the Form 3L.
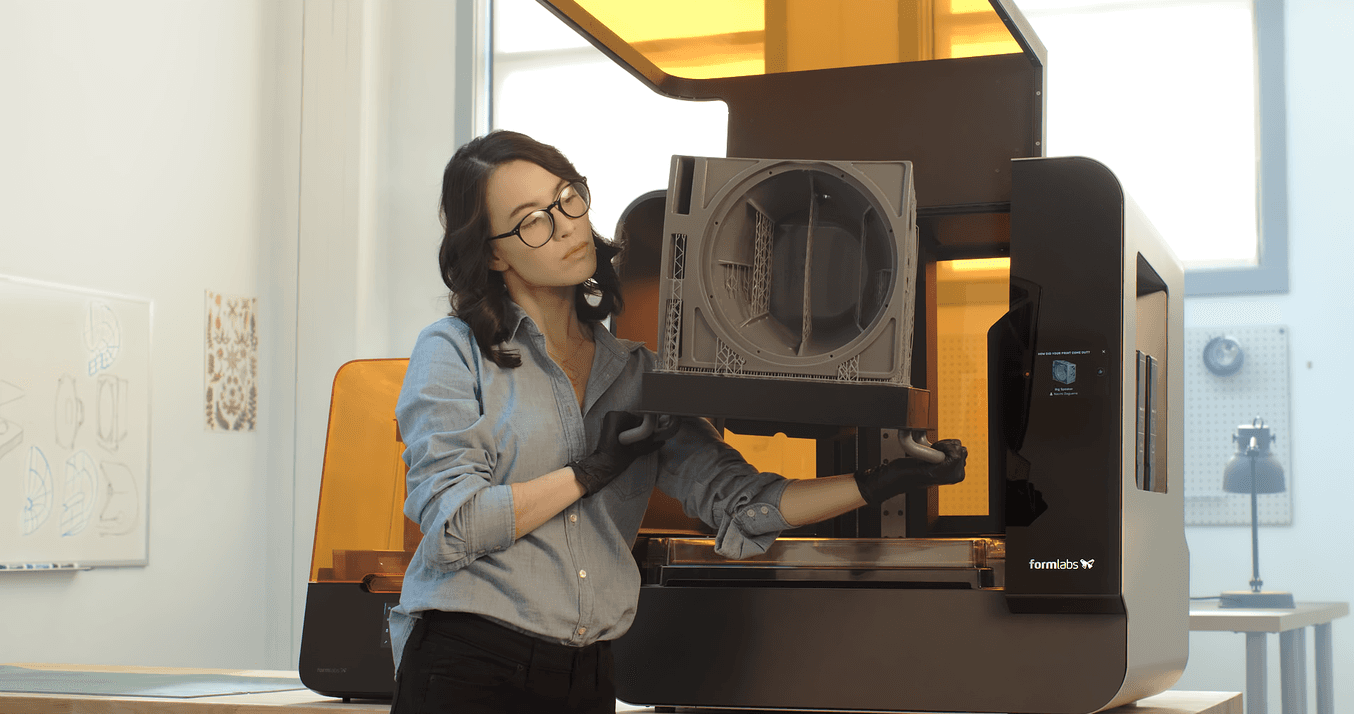
The Form 3L is the first affordable big format SLA 3D printer with a build book of 30 cm 10 33.5 cm x 20 cm.
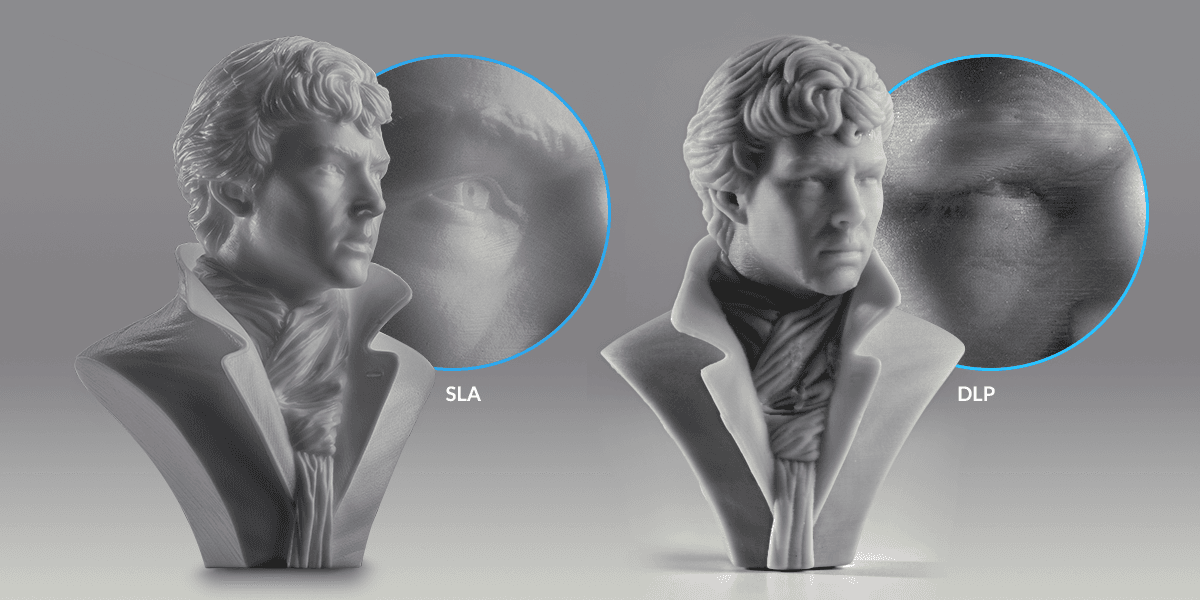
SLA and DLP resin 3D printers both known for creating parts with the smoothest surface finish of all 3D press processes. When we describe the differences, in most cases these are but visible on tiny parts or highly detailed models.
Because objects are fabricated of layers in 3D printing, 3D prints often have visible, horizontal layer lines. However, considering DLP renders images using rectangular voxels, there is also an outcome of vertical voxel lines.
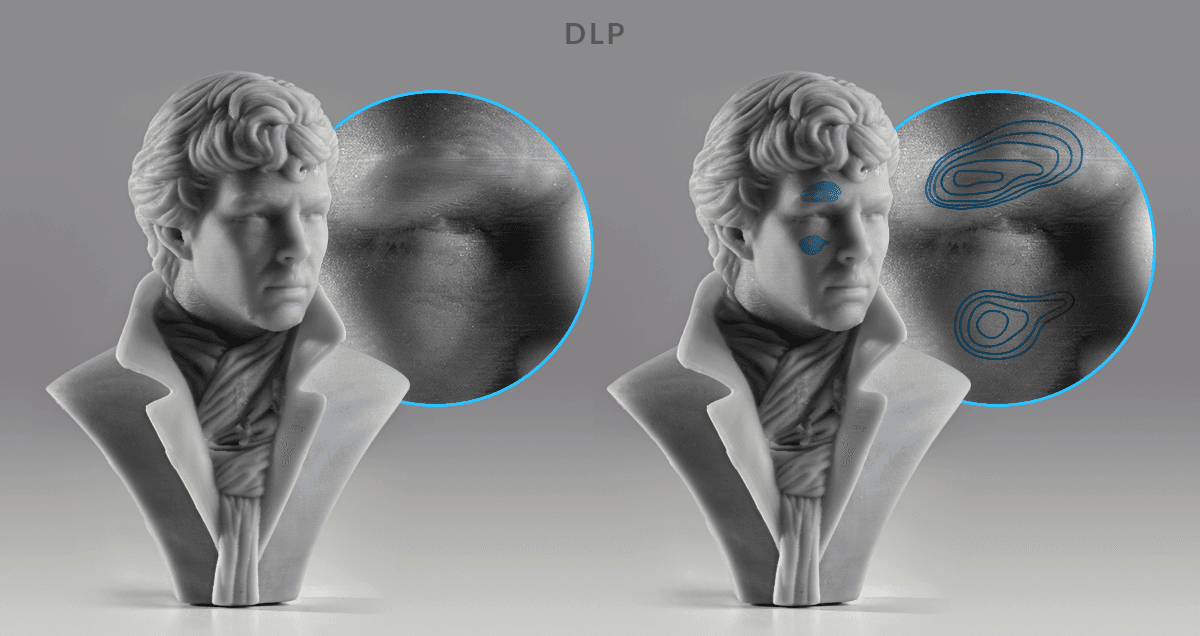
DLP 3D printers render images using rectangular voxels, which causes an result of vertical voxel lines. In this image, run into the vertical voxel lines as they appear naturally on the left, and so outlined to more than hands identify on the right.
Because the unit of measurement is rectangular, voxels also have an upshot on curved edges. Recall of edifice a round shape out of LEGO bricks—the edges will appear stepped on both the Z axis and the 10-Y airplane.
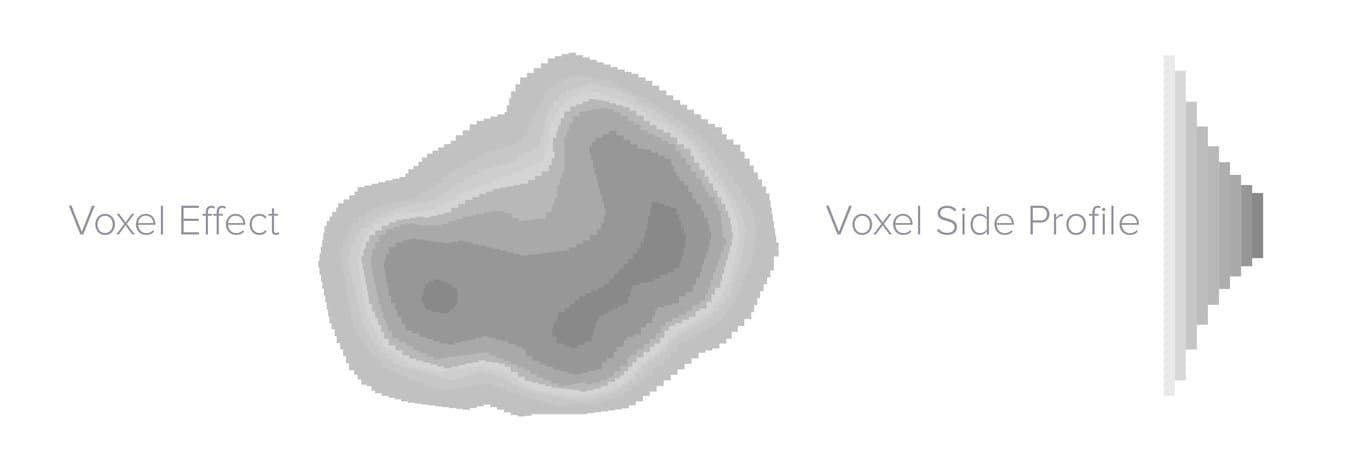
The rectangular shape of voxels makes curved edges announced stepped. Removing the advent of voxel and layer lines requires post-processing, such every bit sanding.
In LFS 3D printing, layer lines are close to invisible. As a result, surface roughness is reduced, which ultimately leads to smooth surfaces, and for articulate materials, more translucent parts.
When thinking about speed in 3D printing, information technology'south important to consider non just raw print speed, but also throughput.
Raw print speed for SLA and DLP resin 3D printers is comparable in general. As the projector exposes each entire layer all at in one case, print speed in DLP 3D press is uniform and depends simply on the height of the build, whereas, SLA 3D printers draw out each part with a laser. As a rule of thumb, this results in SLA 3D printers being comparable or faster when press small or medium-size single parts, while DLP 3D printers are faster to impress large, fully dense prints, or builds with multiple parts that fill up much of the platform.
Simply once more, it's worth because the merchandise-off betwixt resolution and build book for DLP printers. A small DLP 3D printer can print a small part or a (small) batch of smaller parts fast, at loftier resolution, simply the build volume limits the role size and the throughput. A dissimilar machine with a larger build book can print larger parts or a batch of smaller parts faster, but at a lower resolution than SLA.
SLA 3D printers tin produce all of these options in one machine and offer the user the freedom to make up one's mind whether she wants to optimize for resolution, speed, or throughput.
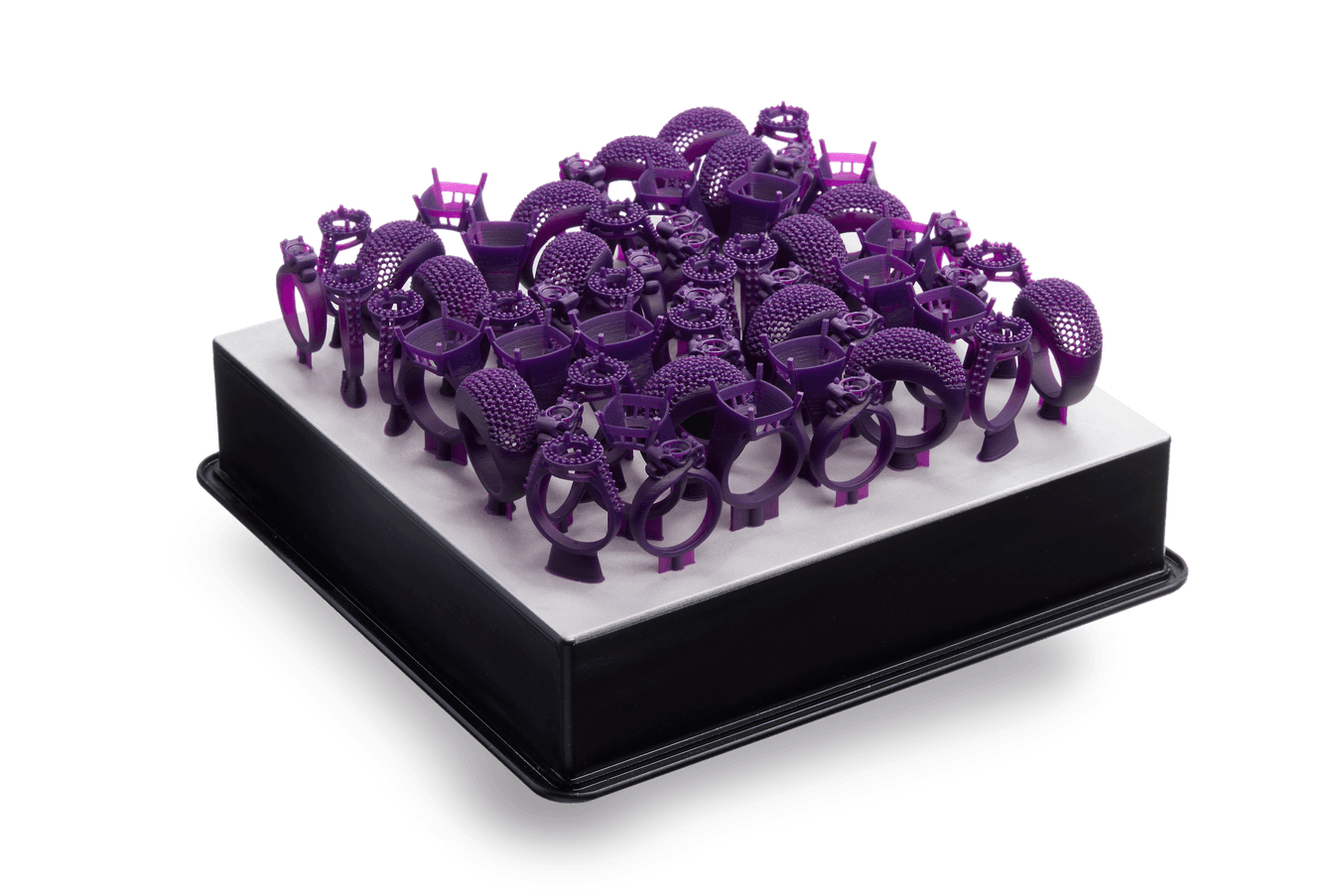

SLA 3D printers offer a larger build volume, assuasive users to batch parts and print overnight to increase throughput.
Speed can also depend on the material pick. Printing 4 times faster than Formlabs standard materials, Draft Resin fast-printing resin that is ideal for initial prototypes, rapid iterations, besides as dental and orthodontic models. From fast print initiation speeds to minimal support removal, wash, and cure times, Draft Resin has an optimized workflow to truly maximize efficiency.

| 100 microns | 200 microns |
|---|---|
| | |

| 100 microns | 200 microns |
|---|---|
| | |

| 100 microns | 200 microns |
|---|---|
| | |
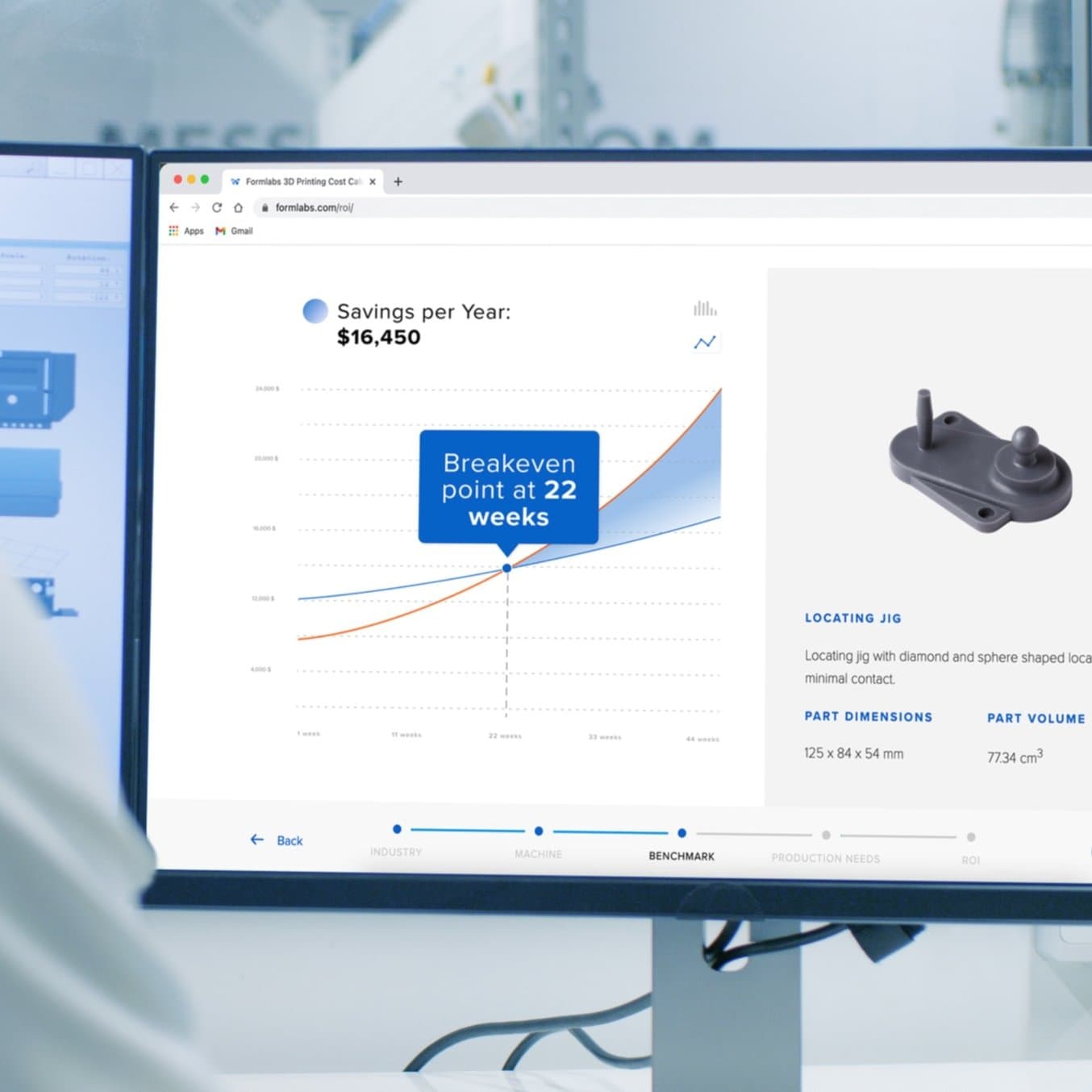
Interactive
Try our interactive ROI tool to see how much time and price you can save when 3D printing on Formlabs 3D printers.
Calculate Your Savings
Just like with accuracy and precision, the workflow and available materials differ more from machine to machine than technology to technology.
Most SLA and DLP 3D printers are "plug and play," with easily swappable build platforms and resin tanks. Some more than avant-garde models as well come with a cartridge organisation to automatically refill the tank with liquid resin, which requires less attention and facilitates printing overnight.
Some printers come with proprietary software to fix 3D models for printing, such as PreForm for Formlabs SLA 3D printers, while other manufacturers offer off-the-shelf solutions. Features differ past software tool, for instance, PreForm offers ane-click print setup, powerful transmission controls to optimize support density and size, adaptive layer thickness, or functions to save material and time. Luckily, the software tin can be easy to download and exam before purchasing a 3D printer.
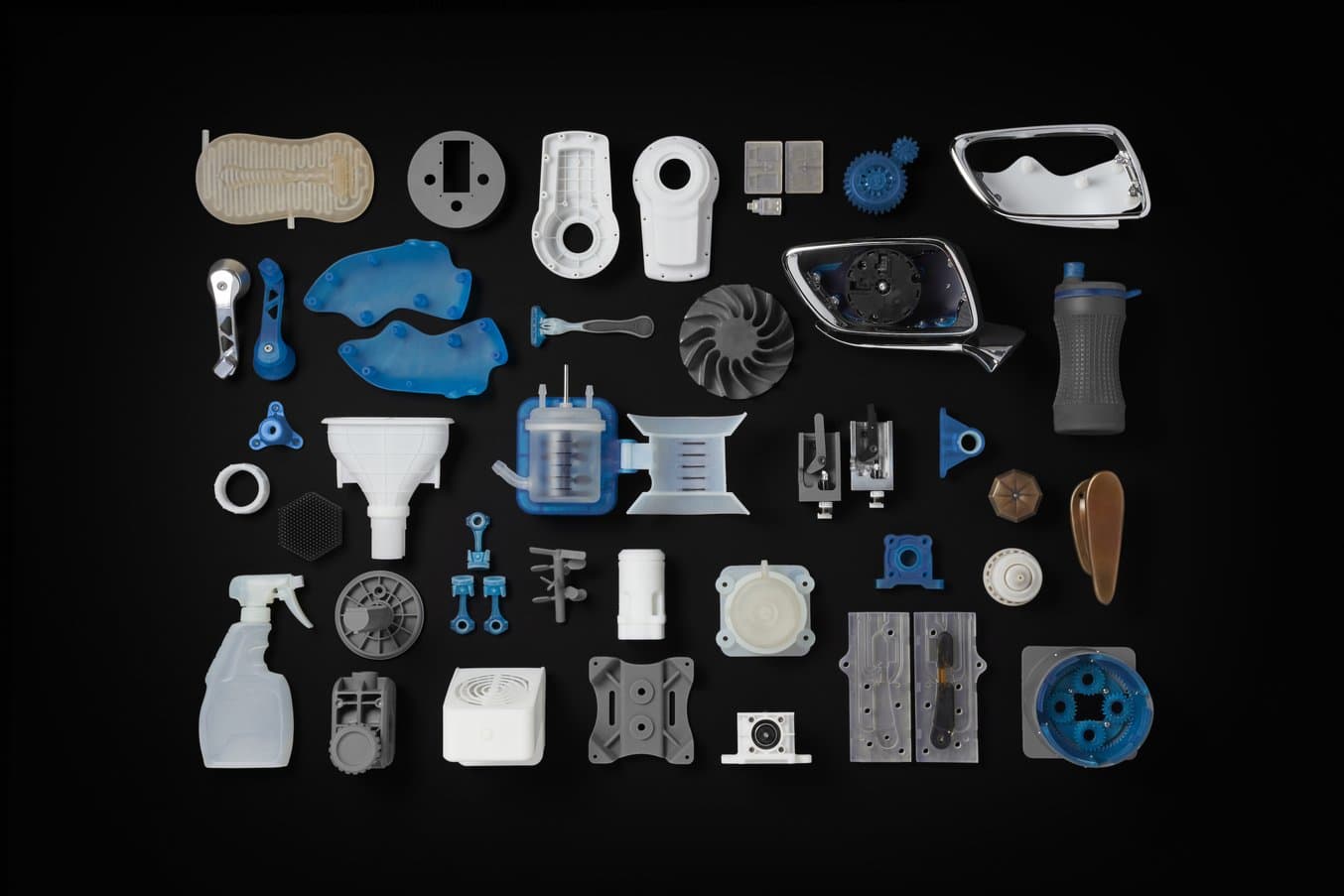

Resin 3D printers offer a variety of materials for a wide range of applications.
Ane of the virtually significant benefits of resin 3D press is the variety of materials that brand it possible to create parts for diverse applications. Resins tin can feature a broad range of formulation configurations: materials can be soft or hard, heavily filled with secondary materials like drinking glass and ceramic, or imbued with mechanical properties like high heat deflection temperature or affect resistance.
Notwithstanding, the range of supported textile options depend on the 3D printer model, then we recommend inquiring with the manufacturer before buy.
Parts printed with both SLA and DLP technologies crave post-processing later press. First, the parts need to be washed in a solvent to remove backlog resin. Some functional materials like engineering or biocompatible parts also crave post-curing. For SLA 3D printers, Formlabs offers solutions to automate these steps, saving time and effort.
At concluding, 3D printed parts printed on supports require these structures to exist removed, a manual process that is similar for both SLA and DLP 3D printers. LFS 3D press simplifies this step by offer light-touch support structures that apply very small touchpoints to enable easy removal with minimal support marks left behind.
Interactive
Need some help figuring out which 3D printing textile yous should choose? Our new interactive material wizard helps you lot make the right material decisions based on your application and the properties y'all intendance the near almost from our growing library of resins.
Recommend Me a Fabric
After sorting out the differences in applied science and outcomes, we hope it's much easier to select a resin 3D printer that best matches your workflow and output needs.
To explore the next generation of SLA 3D printing, learn more about the Form iii and Form 3L LFS 3D printers.
Curious to see the quality immediate? Order a sample part shipped to your part.
olivarezinesepark.blogspot.com
Source: https://formlabs.com/asia/blog/resin-3d-printer-comparison-sla-vs-dlp/
0 Response to "dlp 3d printer pictures drawing"
Kommentar veröffentlichen